IMPACT OF INFLATION ON THE INDIAN ECONOMY (MAY 2018-APRIL 2019)
INFLATION??
Inflation is a quantitative proportion of the rate at which the average price of chosen goods and services in an economy increases over some undefined time frame. It is the consistent increase in the general level of price where a unit of currency buys short of what it did in earlier periods. Frequently communicated as percentage, inflation shows a decrease in the purchasing power of a nation’s currency. A normal inflation rate for a country is about 2-3%. The highest rate that has been ever recorded in the history of India has been September 1974, where the rate touched 34.70%(Source: www.inflation.eu) . The current rate is 3.80%, which implies that the government is printing more money in order to take care of its revenue and expenditure.
CAUSES OF INFLATION:
- Demand pull effect-
When the aggregate demand is greater than aggregate supply, the demand pull situation arises. If this situation arises, it means that the economy is growing at a fast pace. At this stage, if the economy is close to employment or there is full employment, then a rise in aggregate demand leads to a rise in general price level. As firms achieve full employment, they react by setting up costs prompting inflation. Additionally, near full employment with labor deficiencies, workers can get higher wages which increment their spending power. If economic growth is above long run trend rate of growth that’s when demand pull inflation is evident.
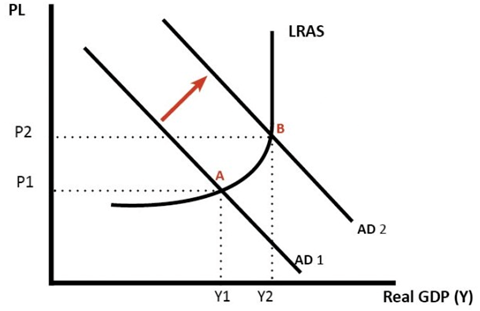
2). Cost push inflation-
An increase in the expenditure made by firms will lead to an increase in prices for buyers also because at this stage the organizations pass the rise in expenses towards the consumers. There will be a leftward shift in the aggregate supply.
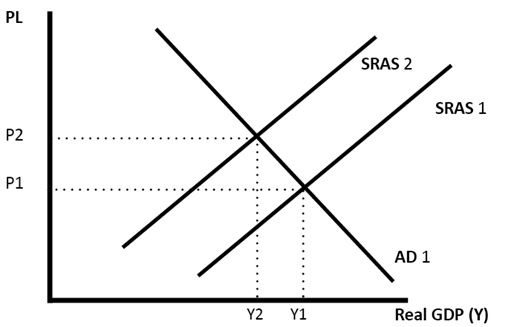
(Source: www.economicshelp.org)
3). Increase in money supply-
An excess money supply situation by the central bank will lead to a rise in inflation and general price levels and this in turn will cause problems to the consumers that exist in the market. If there is excess supply of money, a situation called “Hyperinflation” arises, which is one of the major problems an economy can face.
ADVANTAGES OF INFLATION:
1). Deflation can be a bane-
People tend to postpone their purchases assuming that the prices will decrease in the near future in case of deflation. This leads to a stop in circulation of money causing the economy to fall.
2). No debt burden-
The ideal inflation rate is expected to be 2%, while taking a debt. If the rate deflates instead of inflating, people will further be forced to pay a higher debt. Therefore, it increases their debt burden.
3). Growth boost-
A country suffers from recession when the inflation rates are low. Most of the countries set a target to maintain a moderate rate of inflation so that it can push the circulation of money in the economy.
DISADVANTAGES OF INFLATION:
1). Reduces investment-
If the inflation rates are low then firms take the opportunity to risk and invest, which improves stability but since the future cannot be predicted, people fear investing money and losing it later. This in turn reduces investments.
2). Reduces value of savings-
If interest rates are lower than inflation rate, people who save money are more likely to suffer the most since they do not get the required amount of interest.
3). Uncompetitive economy-
If the inflation rates are high, they can make a country’s economy uncompetitive. It will cause a downfall in exports, thereby leading to a current account deficit and lower economic growth.
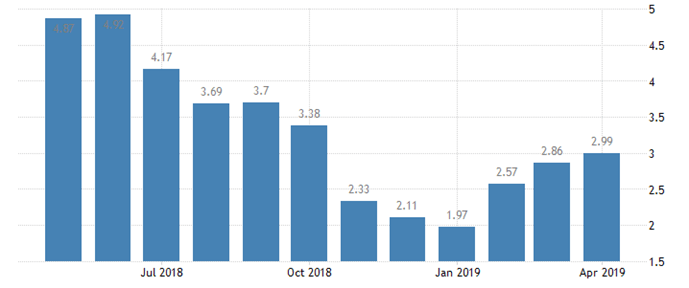
INFLATION RATES (May 2018 – April 2019):
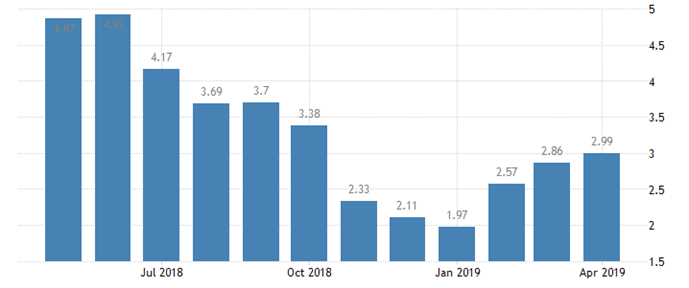
(Source: tradingeconomics.com)
- It is quite clear that there has been a huge difference between the inflation rates from May 2018- April 2019. The fluctuations are evident and the lowest rate between this period has been in January 2019, where the rate has dropped to 1.97%.
IMPACT ON INDIAN ECONOMY:
1). Retail inflation-
The data as per May 2019 is 3.05% (seven-month high). A rise in food and vegetable prices have led to a rise in retail inflation for four continuous months, which is determined based on Consumer Price Index(CPI). (Source: www.businesstoday.in Published: June 12, 2019)
- As per the statistics that have been released by Central Statistics Office (CSO), inflation in food has increased to 1.83% in may and the same was valued at 1.1% in April.
2). Index of Industrial production (IIP)-
- It took a greater step towards change in April 2019 as it grew to an extent of 3.4% as compared to April 2018. This was mostly because of better performance by the mining and power segments.
- When compared to 2018, the industries have shown a great improvement which has led to positive growth. 14 out of 23 industry groups were successful.
- “Textile industry” showed the highest growth at 33.60%.
- “Pulp and paper industry” had achieved the highest negative growth of (-)12.3%. “Metal industry” had also shown negative outcomes, except machinery and equipment @ (-)9.6%. “Transport equipment industry” on the other hand had the lowest negative rate @ (-)3.5%. (Source: www.businesstoday.in Published: June 12, 2019)
3). Effects on goods-
| Goods (April 2019) | Rate |
| Primary goods | 5.2% |
| Capital goods | 2.5% |
| Intermediate goods | 1.0% |
| Infrastructure and construction goods | 1.7% |
| Durable goods and non-durable goods | 2.4% and 5.2% |
(Source: www.businesstoday.in Published: June 12, 2019)
SECTORS BENEFITED DUE TO HIGH INFLATION:
1). Daily utilities-
- They are the necessities of life and even if there is a slight rise or fall in prices they remain constant.
Example- A rise in the price of medicines or water will not affect the consumer because he will have to buy them, the reason being that they are necessary for them.
2). Raw material-
- Since raw materials are essential for production process, manufacturing units have to buy them because the production process does not operate as per hike in prices.
- If there is high inflation there will be high demand for the raw material too.
3). Gold stocks-
- Inflation is the right time for people who have invested in gold and are planning to sell gold.
- The price of gold will hike to a huge margin which will give investors a huge profit for their investment. Keeping the money with them during inflation is not a good idea because the purchasing power of a consumer is being reduced as there is only less value in the currency of the country.
4). Oil stocks-
- The demand will remain positive during the period of high inflation because oil is in demand for vehicles and aircrafts; there is no replacement for the same.
MEASURES TO CONTROL INFLATION:
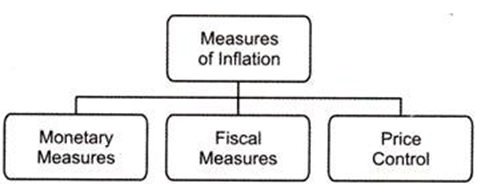
1). Monetary Measures-
- Central bank increases the interest rate on borrowings for commercial banks and because of this commercial banks have to further increase their interest rates for the public.
- Due to this reason people save money instead of investing.
- Monetary measures are further subdivided into Quantitative and Qualitative measures:
- Examples of quantitative measures are Bank rate, Repo rate, Open market operations, Variable reserve ratios etc.
- Examples of qualitative measures are Credit rationing, Regulation of consumer credit, Moral suasion etc.
2). Fiscal Measures-
- The major components of fiscal measures are government revenue and expenditure.
- Government increases taxes on private businesses. If spending is high, the government reduces its expenditure in order to control inflation.
3). Price Control-
- The prices cannot be controlled or suppressed for long term.
- Evidences have shown that price control measure cannot control inflation, it reduces the extent of inflation
CONCLUSION
Inflation is one major issue which affects the Indian economy. The current GDP of India is 7.3%. It is likely to increase to 7.5% in the coming year. With inflation persisting in the economy, it will be difficult for the economy to gain its GDP. Investors should wisely invest in the sectors which would give them adequate returns even if inflation persists in the economy. The RBI should ensure to take proper measures to control inflation so that it can cover up its spending and expenditure.
BIBILOGRAPHY
Media, T. (n.d.). Historic inflation India – CPI inflation. Retrieved from https://www.inflation.eu/inflation-rates/india/historic-inflation/cpi-inflation-india.aspx
India Inflation Rate. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://tradingeconomics.com/india/inflation-cpi
Causes of inflation. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.economicshelp.org/macroeconomics/inflation/causes-inflation/
Great work
LikeLike
Good job,informative and very nicely collect data .Nice work
LikeLike
Nice work, really helpful
LikeLike
Well Written,informative and concise.
Most importantly a pressing issue with regard to the current Economic scenario of India.
LikeLike
Amazing research. Very well written. This is a topic that many of us need to be aware of. Keep up the good work.
LikeLike
Such an informative and amazing work. Nicely put together. Great job.
LikeLike